Sea Moss Gel has risen into the market as a superfood with various potential health and fertility benefits. It is mainly known for its potential to improve fertility in both men and women. As more people turn to natural remedies and holistic approaches to enhance their overall well-being, sea moss gel has emerged as a promising option.
Key Takeaways
- Sea Moss Gel is a superfood that can help boost fertility and expedite pregnancy.
- Sea Moss Gel is an incredibly nutrient-dense food that contains essential vitamins and minerals.
- Sea Moss Gel can help regulate hormones and improve reproductive health.
- You can easily prepare sea moss gel at home and consume it in small doses.
- Spirulina can be taken with Sea Moss Gel to add an excellent source of DHA.
- Sea Moss Gel and Spirulina are safe for consumption during pregnancy and can also benefit children's health.
What is Sea Moss Gel?
Sea moss gel is a jelly-like substance from a seaweed type called Irish moss or Chondrus crispus. You can find it along the rocky shores of the Atlantic coastlines of Europe and North America. Sea moss gel is produced by soaking dried sea moss in water and blending it into a smooth consistency. You can consume this gel-like substance or add it to various recipes as a thickening agent.
There are different types of sea moss, each with its unique properties. Some popular varieties include Irish moss, rich in iodine and minerals; Jamaican sea moss, known for its high nutrient content; and Chondrus crispus, often used for its potential health benefits. Depending on your preferences, you can interchangeably take different types of sea moss to make sea moss gel.
Nutritional Benefits of Sea Moss Gel
Sea moss gel contains an array of essential nutrients that can promote physical health and well-being. It includes a wide range of vitamins, including vitamins A, C, E, and B, such as folate and riboflavin. These vitamins support various bodily functions, including immune system function, cell growth, and energy production.
Sea moss gel is abundant in vitamins and packed with vital minerals like calcium, magnesium, potassium, and iron. These minerals are pivotal in keeping our bones, muscles, and blood circulation top-notch. Moreover, sea moss gel is an excellent source of dietary fiber that facilitates digestion and regulates blood sugar levels.
The combination of vitamins, minerals, and fiber found in sea moss gel makes it a nutrient-dense food that can support overall health. These nutrients also have the potential to improve fertility by providing the body with the necessary building blocks for reproductive health.

Sea Moss Gel and Fertility
| Fertility Benefits | Yes ✅ | No ❌ |
| Increased sperm count | ✅ |
| Improved sperm motility | ✅ |
| Regulated menstrual cycle | ✅ |
| Improved libido | ✅ |
| Increased chances of conception | ✅ |
Research studies conclude promising results regarding the effects of sea moss gel on fertility and conception. One study found that sea moss gel supplementation improved sperm quality and motility in men. Another study on female rats showed that sea moss extract increased the number of viable embryos and improved pregnancy rates.
Sea moss gel can enhance fertility by providing essential nutrients that support reproductive health. The high mineral content, particularly iodine, found in sea moss gel is crucial for proper thyroid function, which is vital in regulating fertility-related hormones. Additionally, the vitamins and antioxidants in sea moss gel can help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, negatively impacting fertility.
How Sea Moss Gel Can Help You Get Pregnant Faster
Sea moss gel can be a valuable tool for individuals trying to conceive by improving fertility and increasing the chances of conception. The nutrients found in sea moss gel support hormonal balance, regulate menstrual cycles and enhance overall reproductive health.
One way sea moss gel can aid in fertility is by promoting a healthy cervical mucus environment. Cervical mucus facilitates sperm transport and survival within the female reproductive system. Sea moss gel's high mineral content helps maintain optimal cervical mucus consistency, making it easier for sperm to reach the egg.
Furthermore, sea moss gel's ability to reduce inflammation and oxidative stress can create a more favorable environment for implantation and pregnancy. By reducing inflammation, sea moss gel may help prevent conditions such as endometriosis and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), which can hinder fertility.
Many women have shared their success stories and testimonials about using sea moss gel to increase their chances of getting pregnant. Cryobank America's Christie Murphy shared her success story after becoming pregnant with twins following a strict sea moss gel regime. These personal experiences highlight the benefits of sea moss gel as a natural fertility aid.
How to Prepare Sea Moss Gel At Home
Making sea moss gel at home is a relatively simple process that requires little ingredients and equipment. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to prepare sea moss gel:
- Start by thoroughly rinsing the dried sea moss to remove debris or impurities.
- Soak the sea moss in clean water for at least 4-6 hours or overnight. This step will rehydrate the seaweed and make it easier to blend.
- Drain the water and transfer the sea moss to a blender after soaking.
- Add fresh water to the blender, using a 1:1 ratio of sea moss to water.
- Blend the mixture at your blender's highest speed until it reaches a smooth, gel-like consistency.
- Pour the sea moss gel into a clean glass jar or container and refrigerate for at least 2 hours to allow it to set.
Dosage and Usage of Sea Moss Gel
The recommended dosage of sea moss gel for fertility and overall health varies depending on individual needs and goals. Start with small servings and gradually increase each serving as tolerated.
A daily dosage of 1-2 tablespoons of sea moss gel should suffice for general health maintenance. However, for individuals specifically targeting fertility enhancement, you speak with a medical professional for guidance and devise a personalized plan.
There are various ways to incorporate sea moss gel into your diet. You can consume it on its own, add it to smoothies, use it as a thickening agent in soups and sauces, or even substitute it for eggs in baking recipes. The versatility of sea moss gel allows for creative and enjoyable ways to reap its benefits.
Precautions and Side Effects of Sea Moss Gel
Although sea moss gel is generally considered safe for consumption, you should consider potential side effects so you can take appropriate measures. When consuming sea moss gel, some individuals report digestive discomfort, such as bloating or gas. You can minimize these symptoms by starting with small amounts and gradually increasing the dosage.
It is also important to note that sea moss gel may interact with certain medications or medical conditions. Due to its high levels of iodine, individuals with thyroid disorders should exercise caution when consuming sea moss gel. Also, if you are pregnant, consult your healthcare provider before incorporating sea moss gel into your diet.
Taking Sea Moss Gel During Pregnancy
Sea moss gel can benefit pregnant women and their developing babies. The high nutrient content, including vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, supports the healthy growth and development of the fetus. Sea moss gel's iodine content is valuable during pregnancy as it contributes to proper brain development in the baby.

Spirulina and Sea Moss Gel — A Great Source For DHA
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is a critical omega-3 fatty acid that propels the structure and function of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina. This vital nutrient is often synthesized from alpha-linolenic acid or obtained from maternal milk (breast milk), fish, or algae.
For vegetarians, vegans, or those who prefer not to consume fish due to dietary restrictions or concerns about pollutants found in some fish, algae-based DHA is an excellent alternative. Microalgae (such as spirulina) from Schizochytrium are particularly good for DHA production. This microalgae is rich in DHA and can be cultivated in controlled environments to produce a high-quality, sustainable source of this essential fatty acid.
The recommended dosage of sea moss gel and spirulina during pregnancy will depend on your needs and medical advice. For personalized guidance, consult with your healthcare professional or prenatal care provider.
Benefits of Sea Moss Gel and Spirulina For Kids
Sea moss gel and spirulina are nutrient-rich superfoods that can offer various health benefits for kids when incorporated into their diet appropriately. You should consult a pediatrician before adding these supplements to a child's diet, especially for children with specific health conditions or allergies. Here are some potential benefits of sea moss gel and spirulina for kids:
Benefits of Sea Moss For Kids
- Rich in Nutrients: Sea moss is a veritable treasure trove of essential minerals and vitamins, including iodine, calcium, potassium, and Vitamin C. These nutrients are vital for promoting healthy growth and development in children.
- Support Immune System: The high vitamin and mineral content in sea moss can help strengthen the immune system, making children less susceptible to infections.
- Promotes Digestive Health: Sea moss is an excellent source of fiber, which is important for digestion and can help alleviate constipation in kids.
- Thyroid Support: The iodine in sea moss is vital for thyroid function, which regulates metabolism, growth, and energy levels.
- Skin Health: Applied topically or ingested, sea moss can help improve skin conditions due to its anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties.
Benefits of Spirulina For Kids
- High in Protein: Spirulina is an excellent source of protein, which helps with growth and repairing tissues in growing children.
- Antioxidant Properties: It contains antioxidants like beta-carotene and Vitamin E that protect against oxidative damage and support the immune system.
- Brain Health: Spirulina's amino acids and essential fatty acids can support brain health, potentially improving focus and cognitive function.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Spirulina has anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce asthma symptoms and allergies in children.
Where Can I Get Sea Moss Gel and Spirulina?
You can purchase sea moss gel and spirulina from many places, online or in physical stores. Here are some options to consider:
- Health Food Stores: Many health food stores carry a wide range of superfoods, including sea moss gel and spirulina. These stores often focus on organic and natural products.
- Online Retailers: Websites like Amazon, eBay, and Etsy have numerous sellers offering sea moss gel and spirulina. You can find these products in different forms (powder, capsules, or raw) and from various brands.
- Specialty Online Stores: Look for online stores specializing in superfoods or specific dietary supplements. Websites like iHerb, Vitacost, or Thrive Market are popular for purchasing health-related products.
- Local Markets or Co-ops: Depending on where you live, local farmers' markets or cooperative grocery stores might sell sea moss gel and spirulina, mainly if they focus on natural or vegan products.
- Pharmacies and Supplement Stores: Some larger pharmacy chains and dedicated supplement stores (like GNC or Vitamin Shoppe) carry a selection of superfoods, including spirulina and sometimes sea moss gel.
- Direct from Producers: Some producers sell directly to consumers through their websites. D2C can be a great way to get fresh, high-quality products from the source.
When purchasing these products online, you should research the seller and read product reviews to ensure they are high-quality. Additionally, if you have any health conditions or are taking medications, it's a good idea to consult a medical professional before incorporating new supplements into your diet.
- Protecting Your Health: Choosing A Sperm Bank Over Natural Insemination
- Hatching a Plan: Learning The Basics About Assisted Hatching in IVF
- Navigating GYN Surgery Before Artificial Insemination
- PGT Testing and Its Role in IVF Treatment
- The Ultimate Guide To Where You Can Donate Sperm In All 50 States
What is CMV?
CMV, cytomegalovirus, is a member of the herpesvirus family and is highly prevalent worldwide. You can become infected with CMV through bodily fluids, including saliva, urine, blood, seminal fluid, and breast milk. The most common transmission modes are through close contact with infected individuals or exposure to bodily fluids. It is important to note that CMV can be present in an individual's body without causing any symptoms or illness, making detecting and preventing transmission challenging.

How Common is CMV?
The CDC states that nearly 1 in 3 children have already been infected with CMV by age 5, and by the age of 40, over half of the population is infected. The prevalence of CMV in sperm donors varies depending on the screened population. Studies have shown that CMV infection rates among sperm donors range from 30% to 70%. However, it is essential to note that the presence of CMV does not necessarily indicate active infection or the potential for transmission. Donor screening protocols typically include testing for CMV antibodies, which can help determine if the donor has contacted the virus in the past.
Symptoms of CMV Infection
CMV infection can manifest differently in individuals depending on their immune system and overall health. Many people infected with CMV may not experience symptoms or only have mild symptoms that resolve independently. However, those with weakened immune systems, such as individuals with HIV/AIDS or undergoing organ transplantation, may develop severe complications. These can include pneumonia, hepatitis, retinitis (inflammation of the retina), and neurological disorders. Awareness of these symptoms and seeking medical attention if necessary is crucial.
Becoming Infected With CMV
Primary CMV infection occurs in people who have never been exposed to the CMV virus before. Once a person becomes infected with CMV, the virus remains alive but dormant inside their body for the rest of their life. Recurrent CMV infection is when a dormant virus becomes active again. CMV infection is usually harmless and rarely causes illness. However, primary CMV infection can cause more severe problems for pregnant women than recurrent CMV infection.
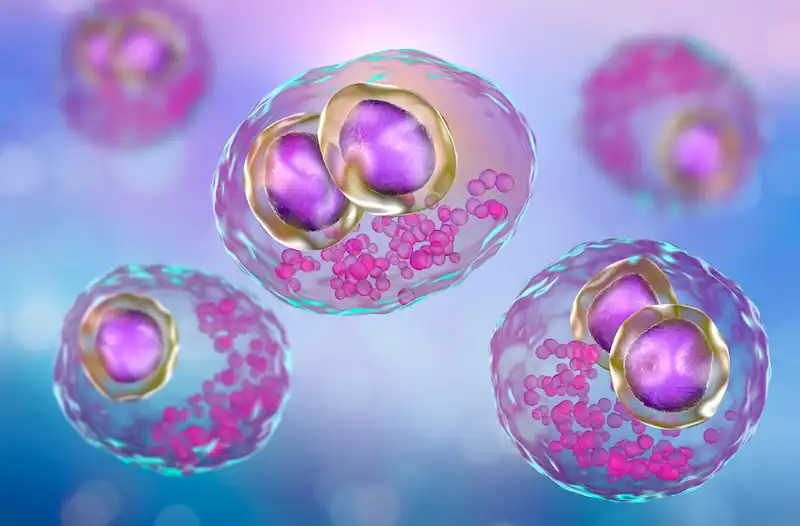
Cytomegalovirus
CMV in human cells.
Diagnosis and Treatment of CMV Infection
Diagnosing CMV infection involves various methods, including blood tests to detect the presence of CMV antibodies or viral DNA. Other tests like urine or saliva samples may also confirm active infection. Treatment options for CMV infection depend on the severity of symptoms and the individual's immune status. A healthcare provider may prescribe antiviral medications to manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications.
Prevention of CMV Transmission in Sperm Donation
Preventing CMV transmission in sperm donation involves following proper protocols and procedures. Donor screening for CMV antibodies is essential in identifying potential donors who may pose a higher risk of transmission. Additionally, implementing strict guidelines for handling and processing donated sperm can help minimize the risk of contamination. Cryopreservation techniques, such as freezing and quarantine periods, can also be employed to ensure that donated sperm is free from infectious agents before use.
CMV Protocols At Cryobank America
The FDA requires CMV testing on all men who intend to donate sperm. A positive result, however, doesn't necessarily mean that a man will be ineligible to donate. Cryobank America will obtain semen samples from potential donors and then quarantine those specimens for at least six months. During that time, the donor may have had CMV antibody levels tested several times. If the antibody tests indicate the possibility of a CMV infection close to the time of the sperm donation, the donor will not be allowed to donate their specimens. If the testing demonstrates inconclusive results, the donor will not be permitted to donate. However, if a donor tests positive for CMV IgG only, indicating a past infection, he will be eligible to contribute. These samples appear in the Cryobank America donor database as CMV-positive.
Can Washed Donor Sperm Transmit CMV?
No, clinically washed sperm is typically free from CMV (Cytomegalovirus) transmission. The sperm-washing process separates sperm from the seminal fluid, which reduces the risk of transmitting infections such as CMV. However, no medical procedure can guarantee 100% elimination of all viruses or infections. You should always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and information.
Considering Pregnancy Through Donor Sperm?
Women considering pregnancy with donor sperm should have CMV antibody testing as part of their IDT. Those with a past infection are at low risk of transmitting CMV infection to a fetus and are at little to no risk if they decide to use a CMV-positive donor.
Women never exposed to CMV should consider using a CMV-negative donor. Even though the risk from a CMV-positive donor is low, it is impossible to determine whether there will be a risk for infection.
Cryobank America's donor catalog has a CMV search filter for positive and negative sperm donors. To find a CMV-negative sperm donor, select negative under the CMV option!
CMV Resources
For additional information on CMV, this link is especially helpful:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cmv/symptoms-causes/syc-20355358
If you have any questions about CMV, please email us at [email protected] or call 817-945-8708; we will be happy to help!
PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) and PFOS (perfluorooctane sulfonate) are a group of manufactured chemicals that have gained significant attention during the 1990s due to their potential impact on reproductive health. Various consumer products use these chemicals, including non-stick cookware, waterproof clothing, food packaging, and firefighting foams. While they are known for their durability and resistance to heat, water, and oil, there are concerns about their long-lasting effects on human health. In this article, we will delve into the world of PFAS and PFOS, exploring their uses, health risks, and, specifically, how they can affect fertility in both men and women.
Key Takeaways
- PFAS and PFOS are chemicals commonly found in consumer products, soil, air, tap water, and drinking water.
- Exposure to PFAS and PFOS can lead to fertility issues in both men and women.
- PFAS and PFOS can also impact pregnancy and child development.
- It is difficult altogether to avoid exposure to PFAS and PFOS in modern society.
- Reducing exposure includes using water filters and avoiding products with PFAS and PFOS.
Understanding PFAS and PFOS: What Are They?
PFAS stands for per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. These chemicals contain strong carbon-fluorine bonds, making them highly resistant to environmental degradation. PFOS stands for perfluorooctanesulfonic acid. It is a synthetic chemical compound that belongs to a group of chemicals known as PFAS. Invented by DuPont and first utilized by The 3M Company, PFOS has been added to industrial applications since the 1950s. It began with everyday products such as stain-resistant fabrics, carpet treatments, and fire-retardant foams.
The Widespread Use of PFAS and PFOS in Consumer Products
The use of PFAS and PFOS is pervasive in our daily lives. Due to their unique properties, they're in an extensive range of consumer products. Non-stick cookware is one example where these chemicals reside, creating a surface that repels food and prevents sticking. Waterproof clothing also contains PFAS and PFOS to provide resistance against water and stains. Additionally, food packaging materials such as microwave popcorn bags and fast-food wrappers often contain these chemicals to prevent grease from seeping through.
The Health Risks Associated with PFAS and PFOS Exposure
| Health Risk | Description |
| Cancer | Exposure to PFAS and PFOS can increase the risk of kidney, testicular, and thyroid cancer. |
| Immune System Dysfunction | Exposure to PFAS and PFOS can compromise the immune system, rendering individuals more vulnerable to infections and illnesses. |
| Developmental Issues | Exposure to PFAS and PFOS during pregnancy can lead to developmental issues in infants, including low birth weight and delayed development. |
| Liver Damage | Exposure to PFAS and PFOS can cause liver damage and an elevated risk of liver disease. |
| Hormonal and Reproductive Issues | PFAS can interfere with the normal functioning of hormones in the body, potentially leading to disruptions in the endocrine system. This can result in reproductive problems, thyroid dysfunction, and other hormonal imbalances. |
| Kidney Disease | Some research suggests long-term exposure to PFAS may be associated with kidney damage and an increased risk of kidney disease. |
| Elevated Cholestrol Levels | Studies have found a positive association between PFAS exposure and increased levels of cholesterol in the blood, which can contribute to cardiovascular diseases. |
Exposure to PFAS and PFOS causes a range of health risks. These chemicals accumulate in the body over time, leading to potential long-term effects. They can disrupt hormone levels, affect immune function, and increase the risk of certain cancers. Additionally, these chemicals are associated with liver damage, kidney disease, and developmental issues in children.

How PFAS and PFOS Affect Reproductive Health and Fertility in Men and Women
The impact of PFAS and PFOS on fertility is a growing concern. Research has shown that exposure to these chemicals can have adverse consequences on both male and female reproductive systems. In men, studies have found a correlation between high levels of PFAS and PFOS in the blood and decreased sperm quality, including reduced sperm count, motility, and morphology. In women, exposure to these chemicals can cause menstrual irregularities, diminished ovarian reserve, and an increased risk of infertility.
The Connection Between PFAS and PFOS Exposure and Infertility
The connection between PFAS and PFOS exposure and infertility lies in their ability to disrupt hormone levels and reproductive function. These chemicals can disrupt the production and regulation of hormones, including estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, which are important in maintaining normal reproductive functions. By disrupting these hormonal pathways, PFAS and PFOS can impair ovulation, sperm production, fertilization, implantation, and overall reproductive success.
The Impact of PFAS and PFOS on Pregnancy and Child Development
Pregnant women exposed to PFAS and PFOS may experience adverse outcomes for both themselves and their developing fetus. Research has indicated that women with elevated levels of these chemicals in their bloodstream are at a heightened risk for pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, low birth weight, and preterm birth. Furthermore, exposure to PFAS and PFOS can cause developmental issues in children, including delayed growth, reduced immune function, and neurobehavioral problems.
The Difficulty of Avoiding PFAS and PFOS Exposure in Modern Society
Due to their extensive usage and long-lasting presence in the environment, avoiding exposure to PFAS and PFOS is challenging. These chemicals can enter our bodies through various routes, including ingestion, inhalation, and dermal absorption. They are in everyday products such as food, water, personal care items, and household goods. Additionally, PFAS and PFOS can contaminate the air, soil, and water sources, further increasing the risk of exposure. Studies have verified that PFAS in rainwater samples from various locations worldwide exceed regulatory limits.
PFAS and PFOS in Tap Water
One significant source of PFAS and PFOS exposure is tap water. These chemicals can contaminate water supplies through industrial discharges, firefighting foam runoff, and using contaminated water sources for drinking. The prevalence of PFAS and PFOS in tap water across the United States is a significant cause for concern. A study executed by the Environmental Working Group (EWG) found that these chemicals were detected in the drinking water of over 30 states, affecting millions of people.
PFAS and PFOS in Bottled Water
While many people turn to bottled water as an alternative to tap water, this may not guarantee safety from PFAS and PFOS exposure. Bottled water can also acquire these chemicals due to various factors, such as the source of the water, the manufacturing process, or the packaging materials used. A study conducted by the EWG found that several popular bottled water brands contained detectable levels of PFAS and PFOS.
The Role of Corporations and Governments in Addressing PFAS and PFOS Contamination
Addressing the issue of PFAS and PFOS contamination requires collective action from both corporations and governments. Corporations are responsible for prioritizing the use of safer alternatives and disclosing the presence of these chemicals in their products. Governments play a critical role in setting regulations and standards for using and disposing of PFAS and PFOS. Some countries have already taken steps to ban or restrict the use of these chemicals, while others are still developing regulations to minimize exposure. Countries that prohibit the production, use, importation, and marketing of PFAS and PFOS are the European Union, Australia, New Zealand, and Norway.
Strategies for Reducing Your Exposure to PFAS and PFOS
While it may be challenging to avoid exposure to PFAS and PFOS, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their exposure.
- Avoid products containing PFAS/PFOS: Look for non-stick cookware, food packaging, and stain-resistant products labeled PFAS-free or PFOA-free.
- Filter your drinking and tap water: Use a water filtration system to remove PFAS/PFOS, such as reverse osmosis systems, to filter your drinking water. Review the product specifications to ensure it is effective against these chemicals. You can also add a whole-home water filtration system to remove PFAS/PFOS and other heavy metals. Filtering all tap water in your home further ensures safety from these chemicals through daily activities, such as hand washing, cooking, bathing, laundry, and washing dishes.
- Limit consumption of contaminated foods: Certain foods, mainly fish and shellfish from contaminated water sources, may contain higher levels of PFAS/PFOS. Stay informed about local advisories and limit consumption accordingly.
- Choose safer personal care products: Read labels and avoid cosmetics, skincare products, and cleaning agents that contain ingredients like fluoro or perfluoro.
- Be cautious with stain-resistant fabrics: Avoid purchasing clothing, carpets, or furniture treated with stain-resistant coatings that may contain PFAS/PFOS.
- Properly dispose of products containing PFAS/PFOS: When discarding items like non-stick cookware or stain-resistant products, follow local guidelines for hazardous waste disposal to prevent environmental contamination.
Review FIGO, HEAL, UCSF, and NRDC's fact sheet to learn more about PFAS and PFOS and how they're working together to raise awareness.
- Protecting Your Health: Choosing A Sperm Bank Over Natural Insemination
- Hatching a Plan: Learning The Basics About Assisted Hatching in IVF
- Navigating GYN Surgery Before Artificial Insemination
- PGT Testing and Its Role in IVF Treatment
- The Ultimate Guide To Where You Can Donate Sperm In All 50 States
The journey of sperm is a fascinating and crucial aspect of human reproduction. To fully comprehend the concept of sperm longevity, you should have a basic understanding of the male and female reproductive systems. The male reproductive system comprises the testes, which produce sperm, and the penis, which is responsible for ejaculation. On the other hand, the female reproductive system comprises ovaries, which produce eggs, and the uterus, where fertilization and pregnancy occur.
Understanding sperm longevity is essential for couples who are trying to conceive. Sperm longevity refers to the length of time that sperm can survive and remain viable in the female reproductive system. This knowledge is crucial because it determines the window of opportunity for fertilization. By understanding how long sperm can survive, couples can better plan their attempts at conception and increase their chances of success.
Key Takeaways
- Sperm can survive for as long as five days in the female reproductive system.
- Factors such as age, diet, and smoking can affect sperm longevity.
- Cervical mucus plays a crucial role in protecting and nourishing sperm.
- Poor sperm longevity can lead to infertility and difficulty conceiving.
- Cryopreservation can extend the lifespan of sperm for future use in fertility treatments.
Sperm Longevity: What Does it Mean?
Sperm longevity refers to the ability of sperm to survive and remain viable in the female reproductive system. After ejaculation, sperm must navigate through various obstacles to reach the egg for fertilization. The longer sperm can survive, the greater the chances of successful fertilization.
Sperm longevity is essential for fertility. If sperm do not survive long enough to reach the egg, fertilization cannot occur. Therefore, understanding and optimizing sperm longevity is crucial for couples trying to conceive.
Factors Affecting Sperm Longevity
Several factors can influence the longevity of sperm in the female reproductive system. Age plays a significant role, as studies have shown that sperm quality and longevity tend to decline with age. Lifestyle factors, including smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, an improper diet, and little exercise, can also negatively impact sperm longevity.
Environmental factors can also affect sperm longevity. Exposure to toxins and radiation can damage sperm cells and reduce their ability to survive. Additionally, certain medical conditions such as varicocele (enlarged veins in the scrotum) and infections can impair sperm longevity.
How Long Does Sperm Live in the Male Reproductive System?
| Stage of Male Reproductive System | Lifespan of Sperm |
| Seminiferous Tubules | Several months to years |
| Epididymis | Several weeks to months |
| Vas Deferens | Several months to years |
| Ejaculatory Duct | Several days to weeks |
| Urethra | Several hours to days |
Sperm production and maturation occur in the testes. It takes roughly 64 days for sperm to mature fully. Once mature, the epididymis, a coiled tube that can be found on the back of each testicle, stores sperm. The epididymis acts as a reservoir for sperm, allowing them to gain motility and become capable of fertilization.
When ejaculation occurs, the epididymis propels sperm into the vas deferens, a muscular tube that moves sperm from the testes to the urethra. During ejaculation, sperm mixes with seminal fluid from the prostate gland and other accessory glands. This mixture, known as semen, is then released through the penis.
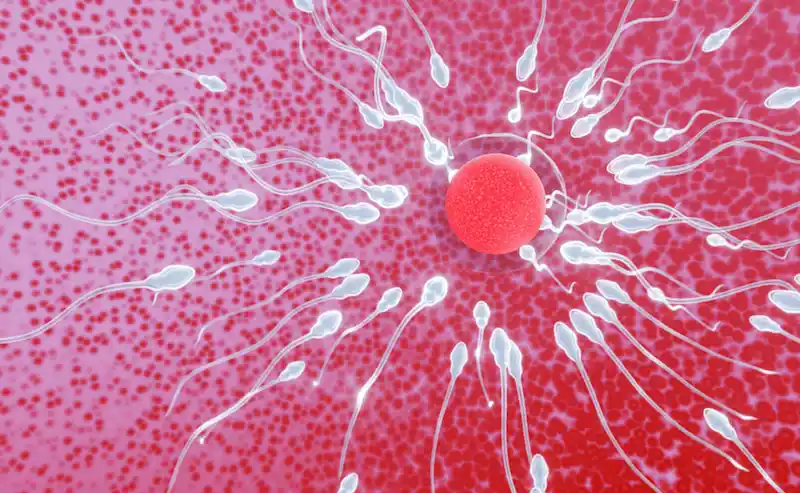
How Long Does Sperm Live in the Female Reproductive System?
After ejaculation, sperm must navigate through the female reproductive system to enter the egg for fertilization. The journey begins with the cervix, which acts as a gateway between the vagina and the uterus. The cervix produces cervical mucus, which plays a crucial role in sperm survival.
Once past the cervix, sperm enters the uterus and continues its journey towards the fallopian tubes. Fertilization typically occurs in the fallopian tubes. Sperm can survive in the fallopian tubes for up to five days, waiting for an egg to be released.
If an egg is present in the fallopian tube during this time, fertilization can occur. The sperm penetrates the egg, forming an embryo. If fertilization does not occur within this window of opportunity, the sperm will eventually die and exit through the body's natural elimination process.
How Cervical Mucus Affects Sperm Survival
Cervical mucus plays a crucial role in sperm survival and fertility. The cervix produces it and changes the menstrual cycle. The consistency and quality of cervical mucus can significantly impact sperm's ability to survive and reach the egg.
During the fertile window, which typically occurs around ovulation, cervical mucus becomes thin, slippery, and stretchy. This type of mucus, often called "egg white cervical mucus," provides an optimal environment for sperm to swim through and survive. It helps nourish and safeguard the sperm and guide them towards the fallopian tubes.
Factors such as hormonal imbalances, specific medications, and infections can impact the quality and quantity of cervical mucus. If cervical mucus is too thick or hostile, it can hinder sperm movement and reduce their chances of survival.
How Long Does Sperm Live Outside of the Body?
Sperm can typically live outside the body for a short period, usually from a few minutes to a few hours. The exact duration depends on various factors such as the environment, temperature, and presence of moisture. However, it is important to note that sperm require specific conditions to survive and thrive and are highly sensitive to changes in temperature and moisture levels. Once outside of the body, sperm gradually lose their motility and ability to fertilize an egg.
Sperm Longevity and Fertility: What's the Connection?
The connection between sperm longevity and fertility is undeniable. For successful fertilization, sperm must survive long enough to reach the egg. If sperm longevity is compromised, it can significantly reduce the chances of conception.
Various factors, including age, lifestyle choices, environmental exposures, and medical conditions, can cause low sperm longevity. If a couple is experiencing fertility issues due to low sperm longevity, treatment options are available. These may include lifestyle changes that improve overall health and medical interventions such as surgery or medication.
Improving Sperm Longevity: Tips for Men
Men can take several steps to improve sperm longevity, increase their chances of conception, and improve sperm health. Lifestyle modifications such as implementing a healthy diet rich in antioxidants and engaging in routine exercise can positively impact sperm health.
Studies show that certain supplements and vitamins can improve sperm quality and longevity. These include valuable antioxidants such as vitamin C, E, and selenium. You should seek approval from a healthcare professional before starting new supplements or medications.
In cases where medical conditions affect sperm longevity, seeking appropriate medical treatment is crucial. Conditions such as varicocele or infections may require surgical intervention or medication to improve sperm health.
Improving Sperm Longevity: Tips for Women
Lifestyle changes can also improve sperm longevity and enhance women's chances of conception. These changes can positively impact fertility, such as maintaining balance and a healthy weight, eliminating stress, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
Certain supplements and vitamins, including folic acid, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids, have been shown to support reproductive health in women. Again, you should consult a healthcare professional before starting new supplements or medications.
If a woman is experiencing fertility issues due to factors such as hormonal imbalances or structural abnormalities, seeking appropriate medical treatment is essential. Treatments may include hormonal therapies, surgical interventions, or assisted reproductive technologies.
Sperm Longevity With Cryopreservation
Cryopreservation is the laboratory process of freezing and storing sperm for future use. This technique has revolutionized fertility treatments by allowing individuals to preserve their fertility for many reasons, such as undergoing medical treatments that may negatively impact fertility or personal choices. It also provides long-term storage for donor sperm.
Cryopreservation can significantly extend the lifespan of sperm. By freezing sperm at ultra-low temperatures, sperm banks can store them for many years without losing their viability. This option allows individuals or couples to use the cryopreserved sperm later when they are ready to conceive.
Cryopreserved sperm can be used in various fertility treatments, including intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilization (IVF). It provides an option for individuals or couples who may not be able to conceive naturally or who wish to delay parenthood.
How Long Does Frozen Sperm Live?
Frozen sperm can remain viable for many years if stored properly. The lifespan of frozen sperm depends on various factors, such as the quality of the sample, the method of cryopreservation, and the storage conditions. Generally, sperm banks or fertility clinics can store frozen sperm for several decades without significant loss of viability. However, the success rates of using frozen sperm decrease over time, so it is best to use the samples within ten years for optimal results. To learn more about Cryobank America's donor sperm and sperm banking options, visit these pages on our website or feel free to contact us!
- Protecting Your Health: Choosing A Sperm Bank Over Natural Insemination
- Hatching a Plan: Learning The Basics About Assisted Hatching in IVF
- Navigating GYN Surgery Before Artificial Insemination
- PGT Testing and Its Role in IVF Treatment
- The Ultimate Guide To Where You Can Donate Sperm In All 50 States
A woman's egg count is crucial in fertility and family planning. This comprehensive blog post will delve into a woman's egg count, exploring its definition, how it is determined, and its significance in fertility. We will also cover factors that can affect a woman's egg count, the impact of age on egg count, and how to test and interpret your egg count. Additionally, we will explore what happens when a woman's egg count is low, whether it is possible to increase it, and the fertility treatments available for women with low egg counts. Finally, we will touch upon egg freezing as a solution for women with low egg counts.
What is A Woman's Egg Count?
A woman's egg count refers to the number of eggs in her ovaries at any time. These eggs are crucial for reproduction as they are released during ovulation so sperm can fertilize them and result in pregnancy. A woman's egg count is discovered through a medical procedure called antral follicle count (AFC), which involves counting the number of small follicles in the ovaries using ultrasound imaging.
Knowing your egg count is vital, as it directly correlates with fertility. A higher egg count generally indicates better fertility potential, while a lower egg count may suggest reduced fertility or potential difficulties in conceiving naturally. A clear understanding of your egg count can enable you to make well-informed choices regarding family planning goals.
How Many Eggs Does A Woman Have?
On average, a woman is born with approximately one to two million eggs in her ovaries. However, this number decreases significantly as she ages. By the time she reaches puberty, only approximately 300,000 to 500,000 eggs remain. The number of eggs continues to decline throughout her reproductive years, with a more rapid decrease occurring after age 35.
It is important to note that every woman is unique, and the number of eggs she has can vary. Some women may have a higher egg count than others, while some may have a lower count. Understanding your egg count can help determine how it may impact your fertility journey.
Factors That Affect A Woman's Egg Count
- Age
- Smoking
- Chemotherapy
- Autoimmune disorders
- Genetic factors
- Environmental toxins
- Obesity
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Endometriosis
Several factors can influence a woman's egg count. Genetic factors play a significant role, as a woman's number of eggs is determined at birth. Some women may have a genetic predisposition to a higher or lower egg count. Unhealthy lifestyle habits, including smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and a poor diet, can harm egg count. Furthermore, medical conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and endometriosis can also affect egg count and overall fertility.
It is essential to be aware of these factors and make conscious choices that promote reproductive health. Quitting smoking or vaping, achieving a healthy weight, and managing underlying medical conditions can help optimize egg count and improve fertility outcomes.

Age and Egg Count: What You Need to Know
Age is one of the most significant factors that affect a woman's egg count. As a woman ages, her egg count naturally decreases due to ovarian aging. This decline in egg quantity is accompanied by a decrease in egg quality, making it more challenging to conceive naturally and increasing the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in embryos.
Understanding the impact of age on egg count is crucial for fertility planning. Women who wish to have children should start their family at a younger age when their egg count and quality are optimal. Delaying pregnancy can significantly reduce the chances of conceiving naturally and may require assisted reproductive technologies through a fertility specialist or OBG-YN.
Do We Have More Time To Conceive Than We Think?
Some evidence suggests that women may be entering Menopause later in life today compared to 20 years ago. Several studies have found a trend towards later age at Menopause in recent years.
For example, a study published in the journal JAMA in 2019 analyzed data from over 16,000 women and found that the average age at natural Menopause had increased by about one year over the past two decades. Another study published in the journal Menopause in 2017 also reported a similar trend of delayed menopause onset.
This shift is unclear, but several factors may contribute to it. Improved healthcare and living conditions, better nutrition, and advancements in medical technology may all play a role. Additionally, women today tend to have fewer children and use hormonal contraceptives more frequently, which could potentially affect their reproductive hormones and delay Menopause.
However, individual experiences of Menopause can vary greatly, and not all women will experience a delay in menopause onset.
How To Test Your Egg Count
There are several methods available to test a woman's egg count. The most common method is antral follicle count (AFC), which involves an ultrasound examination to visualize and count the number of small follicles in the ovaries. Another method is anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) testing, which measures the hormone level produced by the cells surrounding the eggs in the ovaries. Both methods provide valuable information about a woman's ovarian reserve and can help assess fertility potential.
Consult a healthcare provider or fertility specialist when considering testing your egg count. They can guide you in choosing the most appropriate method based on your circumstances and provide an interpretation of the results.
What is a Normal Egg Count?
A regular egg count can vary depending on several factors, including age, genetic predisposition, and individual health. However, as a general guideline, an average egg count is typically around 15 to 30 antral follicles or an AMH level of 1.0 to 4.0 ng/mL. It is important to note that these ranges are not definitive and can vary between individuals.
Genetic predisposition, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions can influence the normal range for each woman. Therefore, it is crucial to have an individualized assessment of your egg count and consult with a healthcare provider or fertility specialist for personalized guidance.
What Happens When A Woman's Egg Count is Low?
When a woman's egg count is low, it can significantly impact her fertility. A low egg count may indicate diminished ovarian reserve, meaning fewer eggs are available for fertilization. Having fewer eggs available can make it more challenging to conceive naturally and may require assisted reproductive technologies such as IVF.
In addition to reduced fertility potential, a low egg count also increases the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in embryos, which can lead to miscarriages or genetic disorders in offspring. It is vital for women with low egg counts to seek medical advice and consult with a fertility specialist to explore their options and discuss the most appropriate treatment plan.
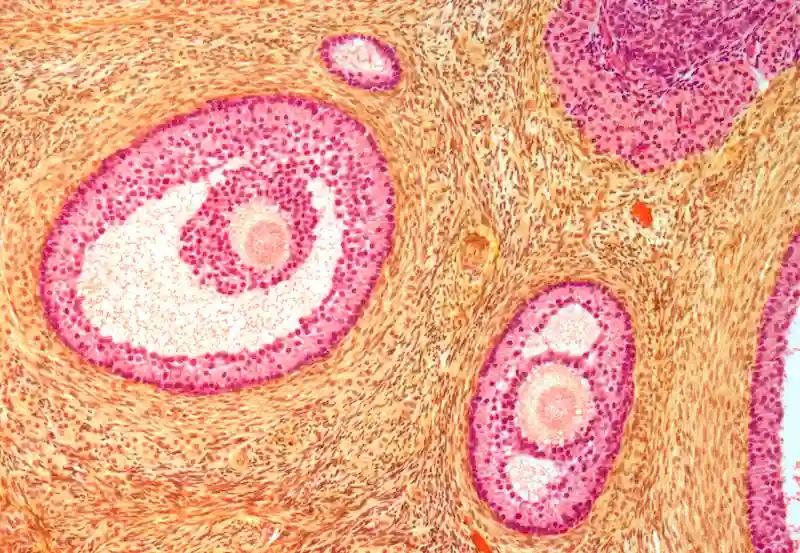
Ovarian Follicles
Light micrograph of a section through secondary follicles in an ovary. Orange: developing eggs (oocytes). Light Pink: fluid-filled cavity (follicular antrum). Dark Pink: granuloma cells.
Why Does a Low Egg Count Increase The Risk of Chromosomal Abnormalities?
Decreased egg count, also known as diminished ovarian reserve, can increase the risk of chromosomal abnormalities in the following ways:
- Advanced maternal age: As women age, the quality and quantity of their eggs decline. Older eggs are more prone to having chromosomal abnormalities, such as aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes). Errors can occur during egg division (meiosis), leading to an unequal distribution of chromosomes.
- Accumulation of genetic mutations: Over time, eggs are exposed to various environmental factors and accumulate genetic mutations. These genetic mutations can affect the integrity of the chromosomes and increase the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Imbalanced hormone levels: Low egg count is often associated with imbalanced hormone levels, particularly follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Elevated FSH levels can indicate decreased ovarian function and reduced egg quality. Hormonal imbalances have the potential to disrupt the natural progression of egg development, leading to an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
- Poor egg quality: Poor egg quality often accompanies diminished ovarian reserve. Poorly developed or immature eggs are more likely to have chromosomal abnormalities. This outcome can be due to impaired DNA repair mechanisms or other cellular processes that ensure proper chromosome segregation during meiosis.
It is important to note that while low egg count increases the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, it does not guarantee that a pregnancy will result in a chromosomally abnormal fetus. However, it does raise the chances, which is why women with diminished ovarian reserve may face difficulties conceiving or have a higher risk of miscarriage or having a child with a chromosomal disorder such as Down syndrome.
Can You Increase Your Egg Count?
While increasing the number of eggs a woman has is impossible, specific lifestyle changes may help optimize egg quality and fertility. Adopting a healthy lifestyle encompassing consistent physical activity, a well-rounded diet, and effective stress management can benefit reproductive health. Furthermore, abstaining from smoking and limiting alcohol intake can enhance fertility outcomes. These lifestyle changes may not directly increase egg count but can create a more favorable environment for the remaining eggs.
Fertility Treatments for Low Egg Count
For women with low egg counts who are struggling to conceive naturally, there are several fertility treatments available. A widely used method in IVF treatment is ovarian stimulation, whereby medications are administered to encourage the ovaries to supply multiple eggs for retrieval. These medications significantly increase the likelihood of successful fertilization and pregnancy.
Another option is donor eggs, where eggs from a young and healthy donor are used for fertilization. Donor eggs can be a viable solution for women with very low egg counts or poor egg quality.
Consider the pros and cons of all treatment options and consult with a fertility specialist to determine the most proactive approach for your unique circumstances.
Egg Freezing: A Solution for Women With A Low Egg Count
Egg freezing, commonly known as oocyte cryopreservation, has emerged as an option for women with low egg counts or those who wish to preserve their fertility for future use. This procedure involves egg retrieval, freezing, and storing for later use.
Egg freezing allows women to preserve their future fertility and potentially increase their chances of successful pregnancy in the future. Consider the benefits and risks, including the cost, success rates, and potential emotional implications. Discussing every aspect with a fertility specialist can provide a comprehensive understanding of egg freezing and help you make an informed decision.
Taking Control of Your Reproductive Health
Understanding a woman's egg count is crucial for fertility planning and taking control of reproductive health. Knowing your egg count empowers you to make informed choices regarding family planning, seek necessary medical advice, and explore various fertility treatment options. You should consult a healthcare provider or fertility specialist who can offer personalized guidance based on your unique circumstances. Taking proactive steps towards understanding and optimizing your reproductive health can increase the chances of achieving your desired family goals.
FAQs
What is a woman's egg count?
A woman's egg count refers to the number of eggs in her ovaries at any given time.
How many eggs does a woman have?
The number of eggs a woman has varies and declines with age. At birth, a baby girl has around 1-2 million eggs. By puberty, this number has decreased to about 300,000-500,000. When a woman reaches Menopause, she may have as few as 1,000 eggs left.
Why is a woman's egg count important?
A woman's egg count is an important factor in her fertility. The more eggs she has, the higher her chances of getting pregnant. A low egg count can make it more difficult to conceive naturally and may require fertility treatments.
How can I find out my egg count?
A woman can determine her egg count through a blood test that measures her anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) levels. This test can estimate the number of eggs a woman has left.
Can a woman increase her egg count?
There is no known way to increase the number of eggs a woman has. However, lifestyle changes can improve overall fertility and egg quality, such as maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol consumption.
What affects a woman's egg count?
The age of a woman is the most crucial determinant of her egg count. Other factors impacting egg count include genetics, medical conditions, environmental factors, and specific treatments such as chemotherapy.
- Protecting Your Health: Choosing A Sperm Bank Over Natural Insemination
- Hatching a Plan: Learning The Basics About Assisted Hatching in IVF
- Navigating GYN Surgery Before Artificial Insemination
- PGT Testing and Its Role in IVF Treatment
- The Ultimate Guide To Where You Can Donate Sperm In All 50 States
The Impact of Supplements on Fertility: What You Need to Know About Harmful Supplements for Fertility
In today's health-conscious world, dietary supplements have surged in popularity. While they intend to enhance one's nutritional intake, a disconcerting truth is that some of these over-the-counter remedies can have deleterious effects on fertility. It's imperative that individuals, particularly those seeking to conceive, be aware of the potential risks.
Most individuals presume that supplements, especially those available without a prescription, are safe. This perception couldn't be further from the truth. As Marta Montenegro, a fertility lifestyles specialist, notes, over 70% of Americans consume supplements that might inadvertently impede their fertility. The reason? These are not mere "gummies"; they carry the weight of medicines, influencing metabolism, hormones, and the critical endocrine system governing fertility.
Further, Dr. Daniel A. Skora, a reproductive endocrinologist, stresses that many supplements, even those sold online, are unregulated. Absent any oversight on dosage or efficacy, the risks amplify.
While many supplements are available, let's delve into those that specialists have identified as potential threats to fertility:
For those trying to conceive, understanding how medications and supplements affect fertility is vital. Here's a closer look at 12 potential culprits, their effects, and alternative considerations.
Medications and Supplements that may Impact Fertility
Alpha Blockers - These are frequently prescribed for urinary problems stemming from an enlarged prostate. However, an unforeseen side effect is that they can affect the process of ejaculation, potentially complicating conception.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy - Aimed at addressing low testosterone levels, this treatment might seem beneficial. However, an unintended consequence is a reduced sperm count or even cessation of sperm production altogether.
Depression Medications - Among the myriad side effects of certain antidepressants, some can disrupt male sexual functions, such as ejaculation. For women, they can tamper with the ovulation process and inadvertently influence hormone levels.
Steroids - Anabolic steroids are notorious for interfering with sperm production in men. In women, some types of corticosteroids can impede the release of hormones pivotal for ovulation.
Thyroid Medication - It's a double-edged sword. While they can be beneficial for fertility, if not accurately dosed, they can disturb prolactin levels, subsequently affecting ovulation.
Antiepileptic drugs & Antipsychotics - Both of these medications have been linked to fertility issues. Not to mention, cancer treatments, especially chemotherapy, have profound, lasting effects on fertility in both genders.
Black Cohosh - Despite its popularity for treating menopausal symptoms, it presents a potential risk. If consumed during pregnancy, it can trigger premature labor.
Vitamin A - A crucial vitamin for numerous body functions. But in high concentrations, particularly during early pregnancy stages, it can induce congenital birth anomalies.
Weight Loss Supplements - A majority have stimulants, which can introduce risks for women contemplating pregnancy.
Megavitamins - It's all about balance. Elevated levels of specific nutrients might compromise a pregnancy's success.
Dong Quai - Renowned as the “female ginseng”, it poses a risk by potentially triggering uterine contractions, upping the odds of miscarriage.
Testosterone Boosting Supplements - In females, they can adversely affect the fetus. In males, they can decrease sperm counts.

Supplements Beneficial for Fertility
Supplements Beneficial for Fertility
Prenatal Vitamins - They're packed with folic acid and iron, both vital during a baby’s early developmental stages. Ideally, women planning to conceive should begin these supplements in advance of pregnancy.
Omega 3 Fatty Acids - They play a multifaceted role. They help regulate hormones, improve the uterus's blood flow, and facilitate embryo implantation. If fish isn't a dietary staple, supplements such as fish or algal oil can suffice.
CoQ10 - Known for its antioxidative properties, CoQ10 has shown promise in enhancing ovarian response and boosting conception rates for women undergoing fertility treatments. It's imperative to consult a healthcare professional before introducing it to your regimen.
Vitamin D - A deficiency in this essential vitamin can be an obstacle to conception. While sunlight and seafood are natural sources, supplements can bridge any gaps, but ensure a doctor's guidance on the correct dosage.
Substances like alcohol, marijuana, and tobacco can also negatively impact fertility. For instance, heavy drinking and smoking can lower testosterone and sperm counts in men and hamper female reproductive health.
Important Note:
Self-diagnosis, driven by symptoms we recognize from online descriptions, can be misleading. Our bodies are complex systems, where symptoms can often indicate multiple conditions. Making assumptions based solely on general information can lead us down a path of incorrect self-treatment, which can, at best, be ineffective and, at worst, harmful. For example, taking a supplement believed to boost fertility based on an article or testimonial without understanding its full effects or interactions with other medications can have unforeseen consequences.
When considering conception, the stakes are even higher. Both partners' health plays a critical role in the likelihood of conceiving and ensuring a healthy pregnancy. Making uninformed changes to medication or supplement intake can not only affect the chances of conception but can also impact the health of the fetus. Certain medications, even those perceived as benign or beneficial, can have teratogenic effects, potentially causing congenital anomalies.
Moreover, everyone's body is unique. A medication or supplement that works wonders for one individual might have a neutral or negative effect on another. This variability can be due to genetics, existing health conditions, lifestyle factors, or other medications being taken. Only a healthcare professional with a comprehensive understanding of an individual's medical history and current state can provide advice tailored to that specific person.
- Protecting Your Health: Choosing A Sperm Bank Over Natural Insemination
- Hatching a Plan: Learning The Basics About Assisted Hatching in IVF
- Navigating GYN Surgery Before Artificial Insemination
- PGT Testing and Its Role in IVF Treatment
- The Ultimate Guide To Where You Can Donate Sperm In All 50 States
Understanding Sperm Count, Morphology, and Motility
When it comes to understanding male fertility, several factors play a crucial role. Among these, sperm count, morphology, and motility stand out as primary indicators of a man's ability to contribute to conception. These terms, often discussed in fertility clinics and significant in the analysis of semen quality, can provide profound insights into male reproductive health.
Sperm Count: The Starting Point
Sperm count refers to the number of sperm cells present in a specific volume of semen. It's a foundational aspect of male fertility, as the quantity of sperm in an ejaculate directly impacts the chances of fertilizing an egg. A low sperm count, a condition known as oligospermia, can signify reduced fertility or, in some instances, infertility. Conversely, a count that's too high can also indicate issues, such as infections. The ideal sperm count for conception is about 15 million sperm per milliliter or more.
Exploring Sperm Morphology: Shape Matters
While numbers are significant, they aren't everything. The shape of the sperm, known as morphology, is equally important. Morphology refers to the size and shape of sperm, and it's critical because it can affect the sperm's ability to reach and penetrate an egg. Normal sperm have an oval head and a long tail, which work together to propel the sperm efficiently toward the egg.
Abnormal sperm morphology (teratospermia) includes defects such as a large or misshapen head, an abnormal midsection, or a crooked or double tail. These defects might impair the sperm's ability to navigate the female reproductive system or penetrate an egg if they do reach it. The percentage of sperm that have a normal shape after ejaculation is thus a key aspect of semen analysis.
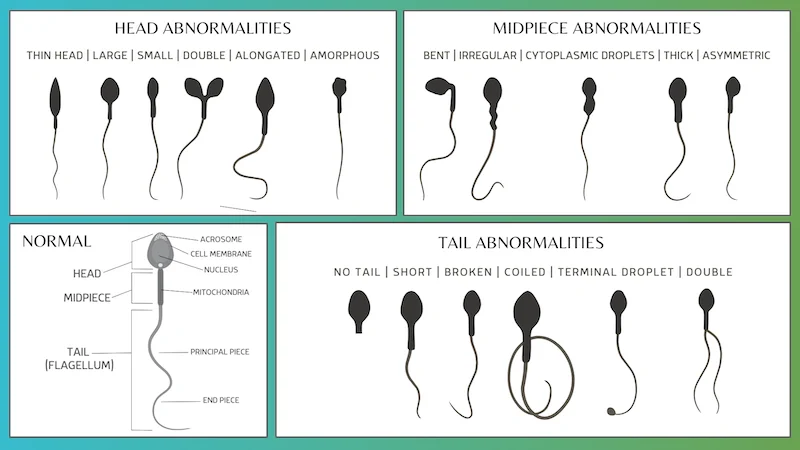
The Role of Sperm Motility: Speed and Direction
However, even if a man has a high sperm count and good morphology, the sperm must be able to move properly — this is where sperm motility comes into play. Motility describes the ability of sperm to move efficiently and is categorized into two groups: progressive motility and non-progressive motility.
Progressive motility refers to sperm that move in a straight line or large circles, while non-progressive motility refers to sperm that do not travel in straight lines or that swim in very tight circles. For conception to occur, sperm must exhibit proper motility to travel through the woman's reproductive tract to reach and fertilize the mature egg. Poor motility (asthenozoospermia) means the sperm struggle to navigate towards the egg, which can be caused by factors like elevated testicular temperature, infection, or exposure to toxic substances.
Interconnection: Count, Morphology, and Motility
These three parameters don't work in isolation; they're interconnected. A semen analysis that shows issues in all three areas (oligoasthenoteratozoospermia) presents a challenging scenario for natural conception and might necessitate advanced reproductive techniques. It's a delicate balance — a high sperm count can offset poor morphology or motility, but excellent motility doesn't make up for a very low sperm count.
Factors Influencing Sperm Health
Several factors can influence sperm count, morphology, and motility. These include lifestyle choices (such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and drug use), environmental exposure to chemicals, stress, and even tight clothing that increases scrotal temperature. Medical issues, like varicoceles (swollen veins in the scrotum) or hormonal imbalances, can also affect sperm health.
Improving Your Sperm Health
Fortunately, many steps can improve sperm health: maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, managing stress, exercising regularly, and avoiding exposure to toxins. Additionally, vitamins and supplements, like Vitamin C, Vitamin D, zinc, and folic acid, have been shown to improve sperm health.
When to Seek Help
While understanding these terms and the conditions they represent is important, it's equally crucial to know when to seek professional help. If a couple has been trying to conceive for a year or more (or six months if the woman is over 35) without success, it's prudent to consult a healthcare provider. They might recommend a semen analysis to evaluate these crucial parameters.
Sperm Health
Sperm count, morphology, and motility are critical pillars of male fertility, each playing a unique role in the conception process. Understanding what they mean and how they impact fertility is the first step for any man looking to start a family. By taking proactive steps to enhance sperm health and seeking help when necessary, men can better navigate the complex journey toward fatherhood.
- Protecting Your Health: Choosing A Sperm Bank Over Natural Insemination
- Hatching a Plan: Learning The Basics About Assisted Hatching in IVF
- Navigating GYN Surgery Before Artificial Insemination
- PGT Testing and Its Role in IVF Treatment
- The Ultimate Guide To Where You Can Donate Sperm In All 50 States
Keto and PCOS
The ketogenic diet, popularly known for its role in weight loss and metabolic health, is emerging as a potential cause for women battling infertility due to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). It comes as a surprise, considering the keto diet is one of the most popular lifestyles, even encouraged by fitness influencers. Considering the growing cases of PCOS in women, there is a dire need to understand the relationship between the keto diet, PCOS, and fertility. This article sheds light on the topic, intending to educate women striving to improve their reproductive health.
PCOS: A Silent Foe of Fertility
PCOS is one of the predominant hormonal disorders in women of reproductive age, notoriously known for interfering with fertility. Women with PCOS contend with irregular menstrual cycles, elevated levels of androgen hormones, and polycystic ovaries. These symptoms pose challenges for conception and elevate risks for other health complications like insulin resistance, obesity, and diabetes.
The Fertility-PCOS Conundrum
One of the primary ways PCOS affects fertility is through irregular ovulation. The hormonal imbalances and insulin resistance associated with PCOS often disrupt the normal ovulation process, making it difficult for women to predict their fertile windows or even experience them. This uncertainty and irregularity are major stumbling blocks for those trying to conceive.
Decoding the Keto Diet
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate lifestyle plan designed to shift the body's metabolism away from carbs and towards fat and ketones. This state, known as ketosis, significantly affects energy usage and hormone regulation, crucial in managing PCOS symptoms.
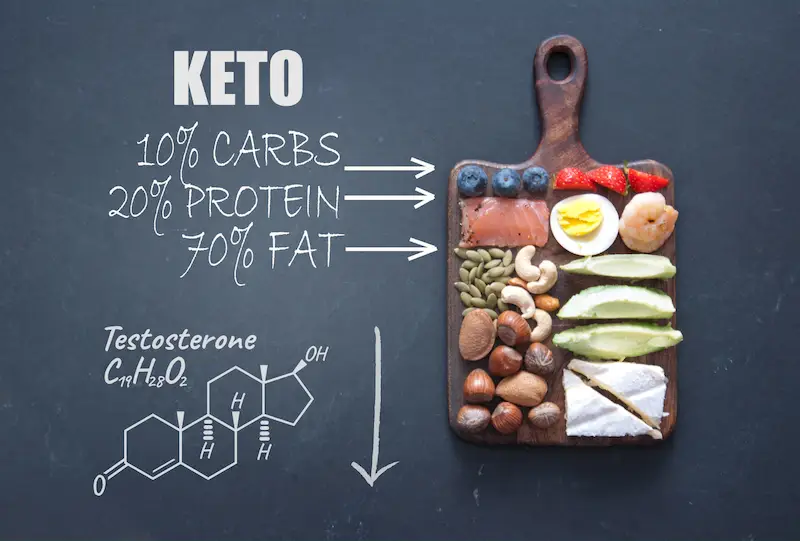
Keto and Hormones: The Biological Crossroad
Insulin plays a villainous role in the PCOS narrative. High insulin levels due to insulin resistance stimulate the ovaries to produce more androgens, such as testosterone, wreaking havoc on the hormonal symphony necessary for ovulation. Here's where the keto diet comes into play. The ketogenic diet can stabilize blood sugar levels, reduce insulin resistance, and potentially lower excessive androgen levels by slashing carbohydrate intake. This restoration of hormonal balance is pivotal in normalizing menstrual cycles and improving fertility outcomes.
Beyond Hormones: The Inflammatory Link
PCOS is also often accompanied by low-grade inflammation, contributing to ovarian dysfunction. The ketogenic diet is noted for its anti-inflammatory effects, thanks to the production of ketones as a byproduct of fat metabolism. By reducing systemic inflammation, the keto diet may further support ovarian function, creating a more conducive environment for ovulation and, consequently, conception.
Real-Life Implications: What Research Suggests
Several studies and anecdotal evidence support the notion that the ketogenic diet can benefit women with PCOS trying to conceive. Research highlights weight loss, reduction in insulin resistance, and improved hormonal balance as some of the benefits of keto that may directly enhance fertility. However, while the existing research is promising, it's still in nascent stages, and more comprehensive studies are required to establish concrete protocols.
Customization and Caution: A Prudent Approach
While the ketogenic diet shows promise in aiding fertility for women with PCOS, it's not without its challenges. Nutrient deficiencies and managing the "keto flu" are concerns that need addressing. Moreover, the diet's restrictiveness can be challenging for many to adhere to long-term. As such, women considering this dietary shift should consult a healthcare provider, preferably one experienced in both PCOS and ketogenic diet guidelines, to create a tailored plan that considers their overall health, nutritional needs, and fertility goals.
Fertility is More Than Diet
It's paramount to remember that while diet is crucial to managing PCOS and enhancing fertility, it's part of a broader picture. Where necessary, lifestyle factors, stress management, consistent physical activity, and medical treatments all weave into the tapestry of fertility enhancement strategies. Women with PCOS should consider a multifaceted approach, focusing on overall health and wellness rather than solely on fertility.
Holistic Strategy For Managing PCOS
The ketogenic diet's potential to boost fertility in women struggling with PCOS lies in its ability to improve hormonal balance, reduce insulin resistance, and mitigate inflammation. While it's not a guaranteed or standalone solution, its incorporation into a holistic strategy for managing PCOS can be a significant step forward for many women. As always, any dietary changes, especially for those with underlying conditions like PCOS, should be undertaken under professional guidance, ensuring a safe and nourishing route toward improved health and fertility.
- Protecting Your Health: Choosing A Sperm Bank Over Natural Insemination
- Hatching a Plan: Learning The Basics About Assisted Hatching in IVF
- Navigating GYN Surgery Before Artificial Insemination
- PGT Testing and Its Role in IVF Treatment
- The Ultimate Guide To Where You Can Donate Sperm In All 50 States
The Science of Sperm Washing: How It's Done and Why It's Important
Sperm washing is a technique used in fertility treatments to separate healthy sperm from other components of semen. It involves removing impurities, such as dead sperm, bacteria, and prostaglandins, from the semen sample. The purified sperm is used in various fertility treatments, such as IUI (intrauterine insemination) or IVF (in vitro fertilization).
The history of sperm washing dates back to the 1980s when it was first developed to reduce the risk of HIV transmission during fertility treatments. At that time, there was a growing concern about the spread of HIV through contaminated semen. Scientists found sperm washing an effective way to remove the virus from the semen, making it safe in assisted reproductive technologies.
Sperm washing is crucial in fertility treatments as it improves the chances of successful conception. By separating healthy sperm from other components of semen, it increases the concentration of motile sperm, which are essential for fertilization. This technique is particularly beneficial for couples with fertility issues, as it allows them to bypass certain obstacles and increase their chances of achieving pregnancy.

The Process of Sperm Washing
Sperm washing involves several steps to ensure the purification of the sperm sample. The process typically begins with collecting a semen sample from the male partner. The scientist or laboratory technician mixes the sample with a solution that helps separate the sperm from other components. They then centrifuge the mixture, which causes the sperm to divide based on density.
Once the sperm separate, they are washed multiple times with a sterile solution to remove any remaining impurities. This process helps improve the quality and concentration of the sperm, making them more suitable for fertility treatments. After washing, the purified sperm can be used immediately or frozen through semen cryopreservation.
The equipment and materials used in sperm washing include a centrifuge machine, sterile containers, and various solutions for washing and preserving the sperm. The centrifuge machine separates the sperm from other components of the semen based on its density. Sterile containers collect and store the purified sperm. The solutions used in sperm washing are unique formulations that remove impurities and preserve the viability of the sperm.
Techniques used in sperm washing may vary depending on the specific fertility treatment. For example, in IUI, the washed sperm is directly injected into the woman's uterus, bypassing the cervix and increasing the chances of fertilization. In IVF, the washed sperm is combined with the woman's eggs in a laboratory dish, allowing for fertilization outside the body.
The Importance of Sperm Washing in Fertility Treatments
Sperm washing is crucial in improving fertility treatments' success rate. Separating healthy sperm from other components of semen increases the concentration of motile sperm, which is essential for fertilization. This technique is particularly beneficial for couples with fertility issues, as it allows them to bypass certain obstacles and increase their chances of achieving pregnancy.
For couples with fertility issues, sperm washing can be a game-changer. It allows them to overcome poor or abnormal sperm motility, morphology, and low sperm count. By purifying the sperm sample, sperm washing increases the concentration of healthy and motile sperm, making it easier to achieve fertilization.
Sperm Washing For Male Infertility and Donor Sperm
Sperm washing is also beneficial for couples with male infertility. In cases where the male partner has a sexually transmitted infection (STI), such as HIV, sperm washing can help reduce the risk of transmission to the female partner and potential offspring. By removing the virus from the semen, sperm washing makes it safe to use in assisted reproductive technologies.
Couples and individuals using donor sperm for insemination also greatly benefit from sperm washing, increasing chances for successful fertilization. Washed sperm samples have a higher success rate; therefore, fewer vials are needed.
How Sperm Washing Helps Prevent Transmission of STIs
One of the significant benefits of sperm washing is its ability to reduce the risk of STI transmission during fertility treatments. When a male partner has an STI, such as HIV, there is a risk of transmitting the infection to the female partner and potential offspring. Sperm washing helps mitigate this risk by removing the virus from the semen.
During sperm washing, the semen sample is thoroughly washed with a sterile solution to remove any viruses or bacteria. This process effectively removes HIV from the semen, making it safe in assisted reproductive technologies. By using purified sperm, the risk of transmitting the infection to the female partner and potential offspring is significantly reduced.
Sperm washing is particularly beneficial for couples with STIs who wish to have children. It allows them to pursue fertility treatments without fearing transmitting the infection. By removing the virus from the semen, sperm washing provides a safe and effective way for couples with STIs to achieve pregnancy.
Sperm washing can prevent the transmission of other STIs, such as hepatitis B and C. By thoroughly washing the semen sample, these viruses are effectively removed, ensuring the safety of the female partner and potential offspring.
Sperm Washing and Genetic Testing
In terms of genetic testing, sperm washing can provide valuable information about the quality and viability of the sperm. Genetic testing can help identify congenital abnormalities or chromosomal disorders that may affect the chances of successful fertilization and pregnancy.
Genetic testing in sperm washing involves analyzing the DNA of the sperm sample to identify any congenital abnormalities or chromosomal disorders. This information can help fertility specialists determine the best option for couples undergoing fertility treatments. For example, if a genetic abnormality is present in the sperm sample, alternative fertility treatments or genetic counseling may be recommended.
Benefits of Sperm Washing For Genetic Testing
The benefits of genetic testing in sperm washing are significant. Fertility specialists can tailor the treatment plan to the couple's needs by identifying congenital abnormalities or chromosomal disorders. Addressing this can increase the chances of successful fertilization and pregnancy and reduce the risk of genetic disorders in potential offspring.
Genetic testing can also help improve the success rate of fertility treatments. By identifying congenital abnormalities or chromosomal disorders, fertility specialists can select the healthiest and most viable sperm for use in assisted reproductive technologies. Addressing this can increase the chances of successful fertilization and pregnancy and reduce the risk of miscarriage or other complications.
Sperm Washing and Gender Selection
Sperm washing can also be used for gender selection, allowing couples to choose the sex of their baby. This technique involves separating sperm based on their X or Y chromosomes, which determine the sex of the offspring. By selecting sperm with the desired chromosome, couples can increase their chances of conceiving a baby of a specific gender.
The benefits of gender selection in sperm washing are significant. It gives couples more control over their family planning and fulfills their desire for a specific gender. Gender selection can be substantial for couples who have a strong preference for a particular gender or who have a family history of genetic disorders that are gender-specific.
Sperm Washing and Assisted Reproductive Technologies
Sperm washing is integral to assisted reproductive technologies (ART), such as IUI and IVF. In IUI, the washed sperm is directly injected into the woman's uterus, bypassing the cervix and increasing the chances of fertilization. In IVF, the washed sperm is combined with the woman's eggs in a laboratory dish, allowing for fertilization outside the body.
The benefits of sperm washing in assisted reproductive technologies are significant. By separating healthy sperm from other components of semen, it increases the concentration of motile sperm, which are essential for fertilization. This technique is particularly beneficial for couples with fertility issues, as it allows them to bypass certain obstacles and increase their chances of achieving pregnancy.
Sperm washing can also improve the success rate of assisted reproductive technologies. By purifying the sperm sample, it increases the chances of successful fertilization and pregnancy. This method can be significant for couples who have been unsuccessful with other fertility treatments or have specific fertility issues requiring a higher concentration of healthy sperm.
The Future of Sperm Washing in Fertility Treatments
Sperm washing has revolutionized fertility treatments and has become an essential technique in assisted reproductive technologies. Its ability to separate healthy sperm from other components of semen has significantly improved the success rate of fertility treatments and has provided hope for couples struggling with infertility.
The future of sperm washing in fertility treatments looks promising. Advancements in technology continue to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the technique. New techniques and equipment are continuously arising to enhance the purification process further and increase the chances of successful fertilization and pregnancy.
Continued research and development in sperm washing technology are crucial to improve fertility treatments further. By understanding the intricacies of sperm biology and developing new techniques, fertility specialists can continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in assisted reproductive technologies.
- Protecting Your Health: Choosing A Sperm Bank Over Natural Insemination
- Hatching a Plan: Learning The Basics About Assisted Hatching in IVF
- Navigating GYN Surgery Before Artificial Insemination
- PGT Testing and Its Role in IVF Treatment
- The Ultimate Guide To Where You Can Donate Sperm In All 50 States
Sperm Health and Genetics
Sperm health is crucial in male fertility and the ability to conceive a child. Various genetic factors significantly affect sperm production, count, motility, and overall quality. Spermatogenesis, responsible for dividing and differentiating germ cells in the testes, produces sperm cells. Various genes control the development and maturation of these cells.
Several genes are involved in sperm production, including those responsible for the formation of sperm cells, the regulation of hormone production, and the maintenance of testicular function. For example, the SYCP3 gene is essential for forming synaptonemal complexes, critical for pairing and recombining chromosomes during meiosis. Mutations in the SYCP3 gene can lead to abnormal sperm production and infertility.

Genetic Factors that Affect Sperm Count and Motility
Genetic factors can have a notable influence on the quantity and movement of sperm. Sperm count refers to the amount of sperm cells in a specific sample, while motility refers to how efficiently the sperm cells move. Both factors play a crucial role in achieving successful fertilization.
Several genetic factors can affect sperm count and motility. For example, mutations in the CFTR gene, responsible for cystic fibrosis, can lead to obstructive azoospermia. This condition is indicated by the absence of sperm in the ejaculate due to blockages in the reproductive tract. Similarly, mutations in the DNAH1 gene, which is involved in the structure and function of sperm tails, can result in immotile cilia syndrome, a condition characterized by the inability of sperm cells to move correctly.
How Genetic Mutations Can Impact Sperm Health
Mutations in the DNA sequence can significantly affect the health of sperm, as they can modify the structure or function of genes. These mutations can either be passed down from parents or arise spontaneously during the production of sperm.
Several genetic mutations can affect sperm health. For example, mutations in the CATSPER1 gene, which regulates calcium channels in sperm cells, can lead to male infertility due to poor sperm motility. Similarly, mutations in the NR5A1 gene, which is responsible for the development and function of the testes, can result in disorders of sex development and infertility.
The Link Between Lifestyle and Sperm Health
Unhealthy lifestyle choices, including smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, and a sedentary lifestyle, can harm sperm health. These factors can lead to decreased sperm count, reduced motility, and lower overall quality.
Smoking, for example, has been shown to reduce sperm count and motility and increase the presence of abnormal sperm cells. Excessive alcohol consumption can also impair sperm production and function. Drug use, particularly anabolic steroids and marijuana, can harm sperm health.
A sedentary lifestyle and obesity also result in poor sperm quality. Lack of physical activity and a low-quality diet can lead to hormonal imbalances and oxidative stress, negatively impacting sperm production and function.
Genetic Testing for Male Infertility
Genetic testing is crucial in diagnosing male infertility and identifying the underlying genetic factors contributing to the condition. Genetic testing can help determine if any genetic mutations or abnormalities may affect sperm health.
Several genetic tests are available for male infertility, including karyotyping, Y chromosome microdeletion analysis, and DNA sequencing. Karyotyping involves examining the structure and number of chromosomes in a person's cells. Y chromosome microdeletion analysis looks for specific deletions in the Y chromosome that can cause male infertility. DNA sequencing involves analyzing the DNA sequence of particular genes to identify any mutations or abnormalities.
Genetic testing offers valuable information about the genetic factors contributing to male infertility. This information can provide beneficial insights for making informed decisions about treatment options and can also help make decisions related to family planning.
The Future of Genetic Research in Sperm Health
Genetic research in sperm health is an active and evolving field. Scientists continually uncover new genes and genetic factors that play a role in sperm production, count, motility, and overall quality. This research is essential for understanding the underlying causes of male infertility and developing new treatments and interventions.
Advancements in genetic technologies, such as next-generation sequencing and gene editing techniques like CRISPR-Cas9, are revolutionizing the field of reproductive genetics. These technologies allow researchers to study the genetic basis of male infertility in more detail and develop targeted therapies to address specific genetic mutations or abnormalities.
How Epigenetics Affects Sperm Health
Epigenetics refers to changes in gene expression that do not involve alterations in the underlying DNA sequence. Various factors, including environmental exposures, lifestyle choices, and aging, can influence epigenetic modifications.
Epigenetic factors can have a significant impact on sperm health. For example, studies have shown that exposure to heavy metals, pesticides, and other environmental toxins can lead to epigenetic changes in sperm cells, affecting sperm count, motility, and overall quality.
Similarly, lifestyle choices such as diet and exercise can influence epigenetic modifications in sperm cells. A healthy diet rich in nutrients and antioxidants can promote positive epigenetic changes, while a poor diet high in saturated fats and processed foods can lead to adverse epigenetic modifications.
The Importance of Genetic Counseling for Couples with Fertility Issues
Genetic counseling is an essential component of managing couples with fertility issues. It involves the assessment of a couple's genetic history, identifying any potential genetic risks, and providing information and support regarding reproductive options.
Genetic counseling can help couples understand the impact of genetics on their fertility and make informed decisions about family planning. It can also provide valuable information about the likelihood of passing on genetic conditions to future children and the available options for genetic testing and assisted reproductive technologies.
- Protecting Your Health: Choosing A Sperm Bank Over Natural Insemination
- Hatching a Plan: Learning The Basics About Assisted Hatching in IVF
- Navigating GYN Surgery Before Artificial Insemination
- PGT Testing and Its Role in IVF Treatment
- The Ultimate Guide To Where You Can Donate Sperm In All 50 States

